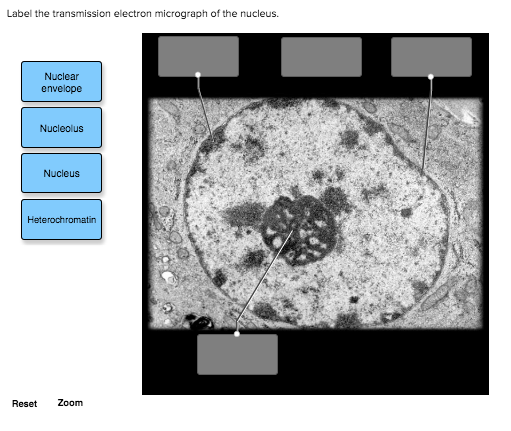
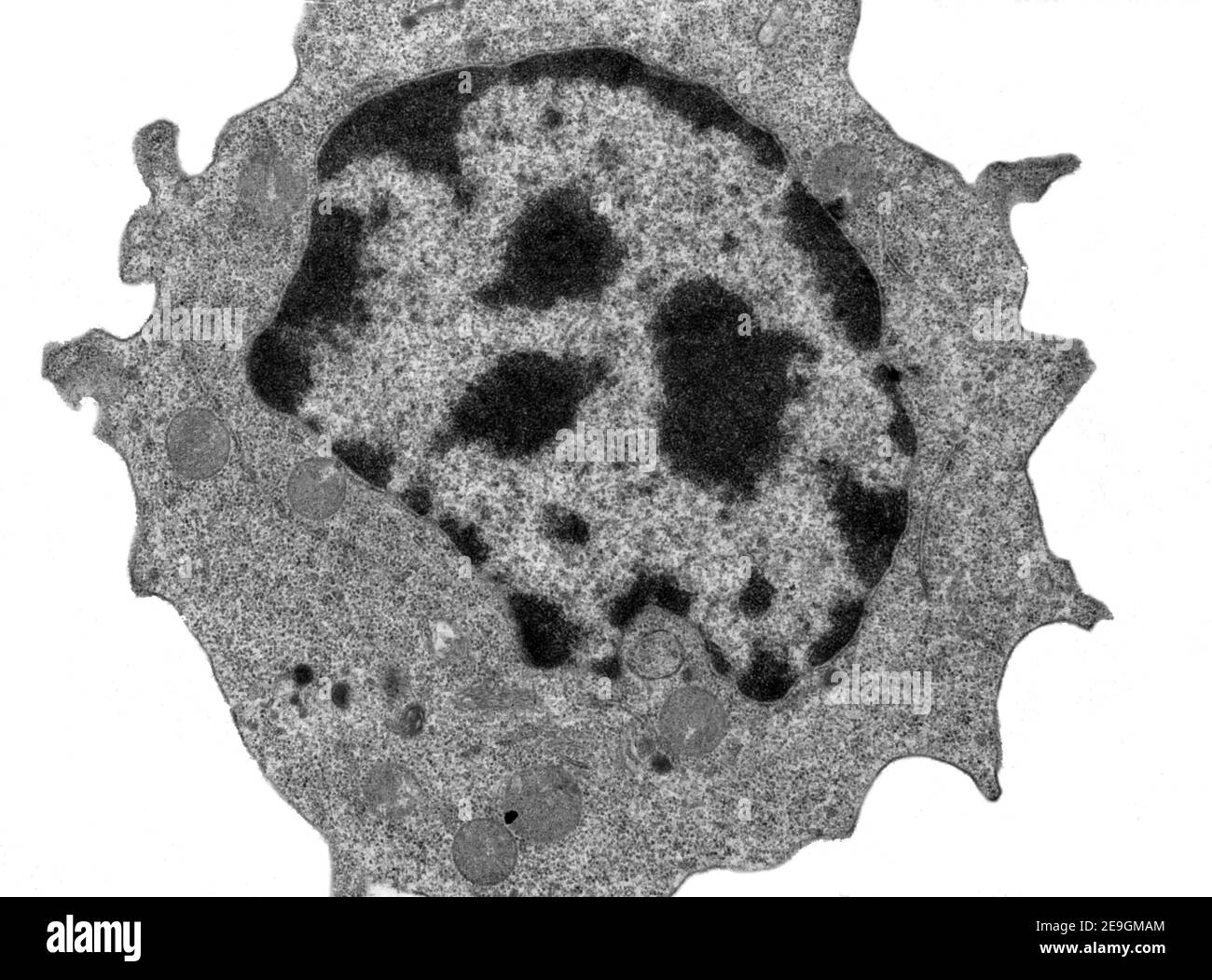
41 label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus
Label This Transmission Electron Micrograph Of A Relaxed ... - Blogger Label this transmission electron micrograph of relaxed sarcomeres by clicking and dragging the labels to the correct location . Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. From science 101 at university high school, tucson. Electron micrographs of relaxed and contracted muscle fibres. Label This Transmission Electron Micrograph / Microscopy Innovations ... Label This Transmission Electron Micrograph / Microscopy Innovations Transmission Electron Microscopy Tem - Abbie Bryan To leave a comment, click the button below to sign in with Google. Sign in with Google Join Our Newsletter
Label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus. - Transtutors Label this transmission electron micrograph of relaxed sarcomeres by clicking and dragging the labels to the correct location Sarcamere 1 band (light) Z disc Mline Aband (dark) H zone Posted 4 months ago View Answer Q: 1. Why do you think RBs have been so difficult to study? 2.

Label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus
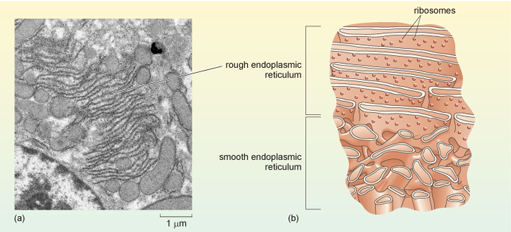
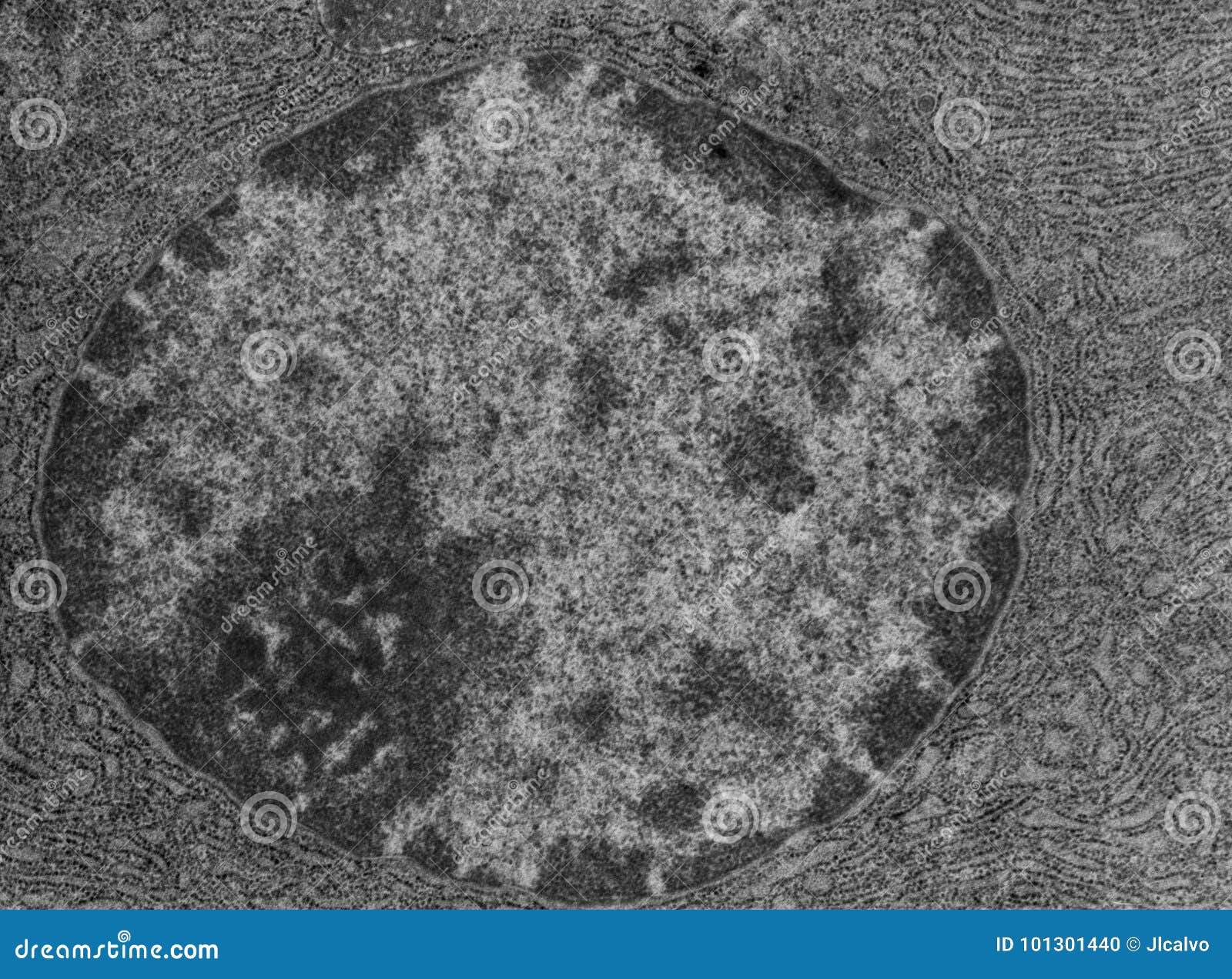
Electron Micrographs of Cell Organelles | Zoology - Biology Discussion The Electron Micrograph of Nucleus: This is an electron micrograph of nucleus. (Fig. 17 & 18): (1) Nucleus was discovered by Brown (1831). (2) It is a characteristic entity of almost all eukaryotic cells except mammalian RBCs. (3) The nucleus is generally one but may also be two, four or many. Peripheral Nervous System | histology - University of Michigan Also, note the nucleus and cytoplasmic organelles of the Schwann cell. Remember that the myelin is part of the Schwann cell, not of the axon. 55 Peripheral nerve - Unmyelinated Nerve Fibers - Cross Section View Virtual EM Slide Unmyelinated Nerve Fibers (cross section). The axons seen in this electron micrograph are all non-myelinated. Electron Microscopic Structure of a Typical Bacterial Cell Under electron microscope the nucleoid appears to be fibrillar and composed of a double or single stranded DNA. It has approximately 5 x l0 6 base pairs and a molecular weight of about 3 x l0 9 . The DNA molecule is approximately 1000 µm long, usually forming ring like structure or sometimes remains diffused throughout the cytoplasm of the cell.
Label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus. (PDF) Cambridge International AS and A Level Biology ... • Enzymes are globular proteins; the basic building blocks of enzymes are amino acids • Their manufacture is controlled by nucleus • Are needed only in small amounts • Enzymes are biological catalysts; they control the rate of a reaction, but are chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction • Enzymes are specific, they affect only ... Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)- Definition, Principle, Images Parts of Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Their working mechanism is enabled by the high-resolution power they produce which allows it to be used in a wide variety of fields. It has three working parts which include: Electron gun Image producing system Image recording system Electron gun Label the Transmission Electron Micrograph of the Nucleus Label the Transmission Electron Micrograph of the Nucleus Study/ By Iris J. Brown Label the Transmission Electron Micrograph of the Nucleus Viewing of objects which are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microscopic examination in a biochemical laboratory Microscopy Nucleus. tem. False colour transmission electron microscope (tem ... False colour transmission electron microscope (TEM) micrograph of an oogonium showing the nucleus (green), the nuclear envelope (pink) and an atypical nucleolus (dark blue). In the cytoplasm (light blue), there are mitochondria (red) and lipid droplets (yellow). x5,000.
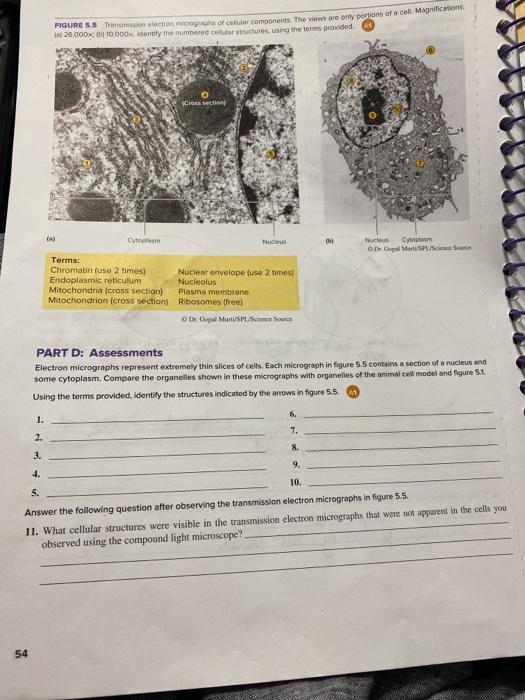
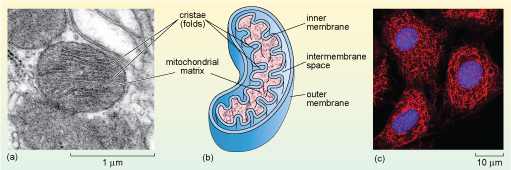
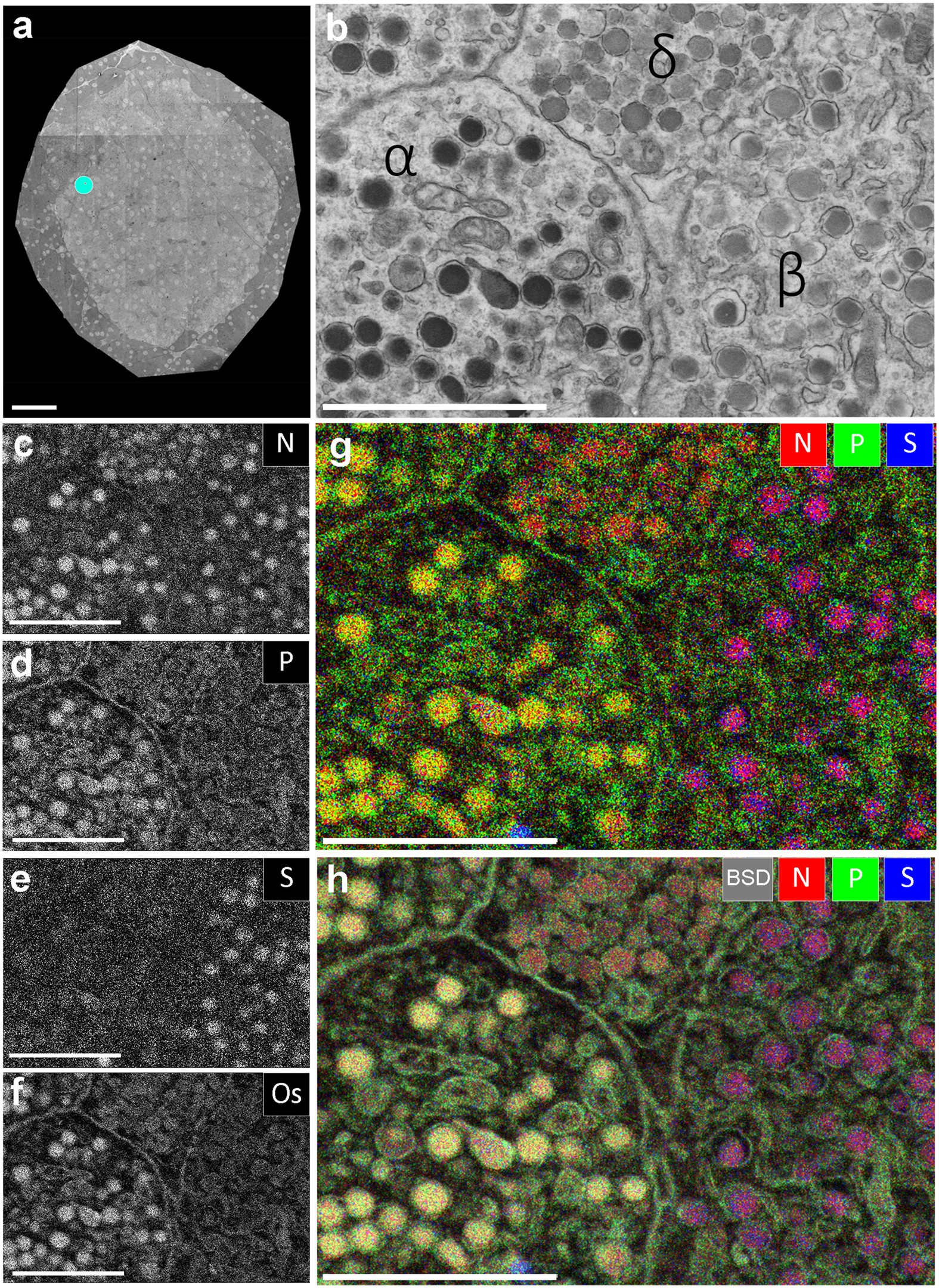
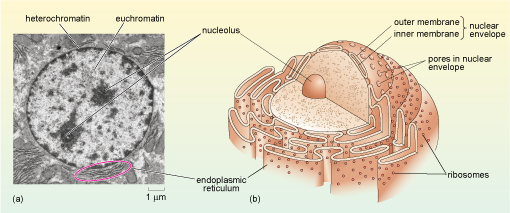
Electron Micrographs - University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center You should concentrate on the similarities in form that permit identification of the components irrespective of cell type. Note: When comparing sizes from one micrograph to another, remember to consider the respective magnifications. Figure 1 Micrograph of a nucleus. 1. Heterochromatin 2. Euchromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleolar associated chromatin HIV/AIDS - Wikipedia HIV/AIDS; Other names: HIV disease, HIV infection: The red ribbon is a symbol for solidarity with HIV-positive people and those living with AIDS.: Specialty: Infectious disease, immunology Label This Transmission Electron Micrograph - Observation on three ... Label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus. ImagiNations - Cool Magnified Images from Figures label this transmission electron micrograph ( 16, . Transmission electron microscopy (tem) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. Cell Nucleus - function, structure, and under a microscope The double membrane system of the nuclear envelope (outer and inner membranes) is discovered by the transmission electron microscopic image below. You can see some gaps between the nuclear envelope; these are nuclear pores, like channels that allow transportation of molecules such as RNAs between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
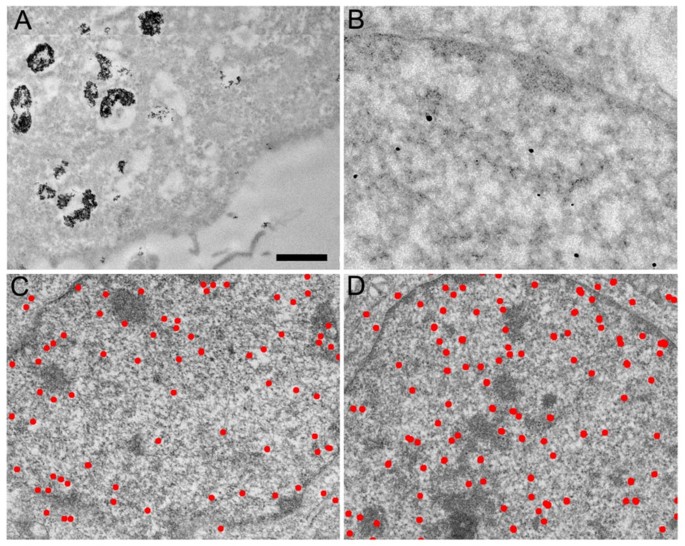
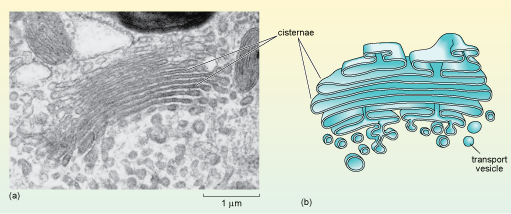
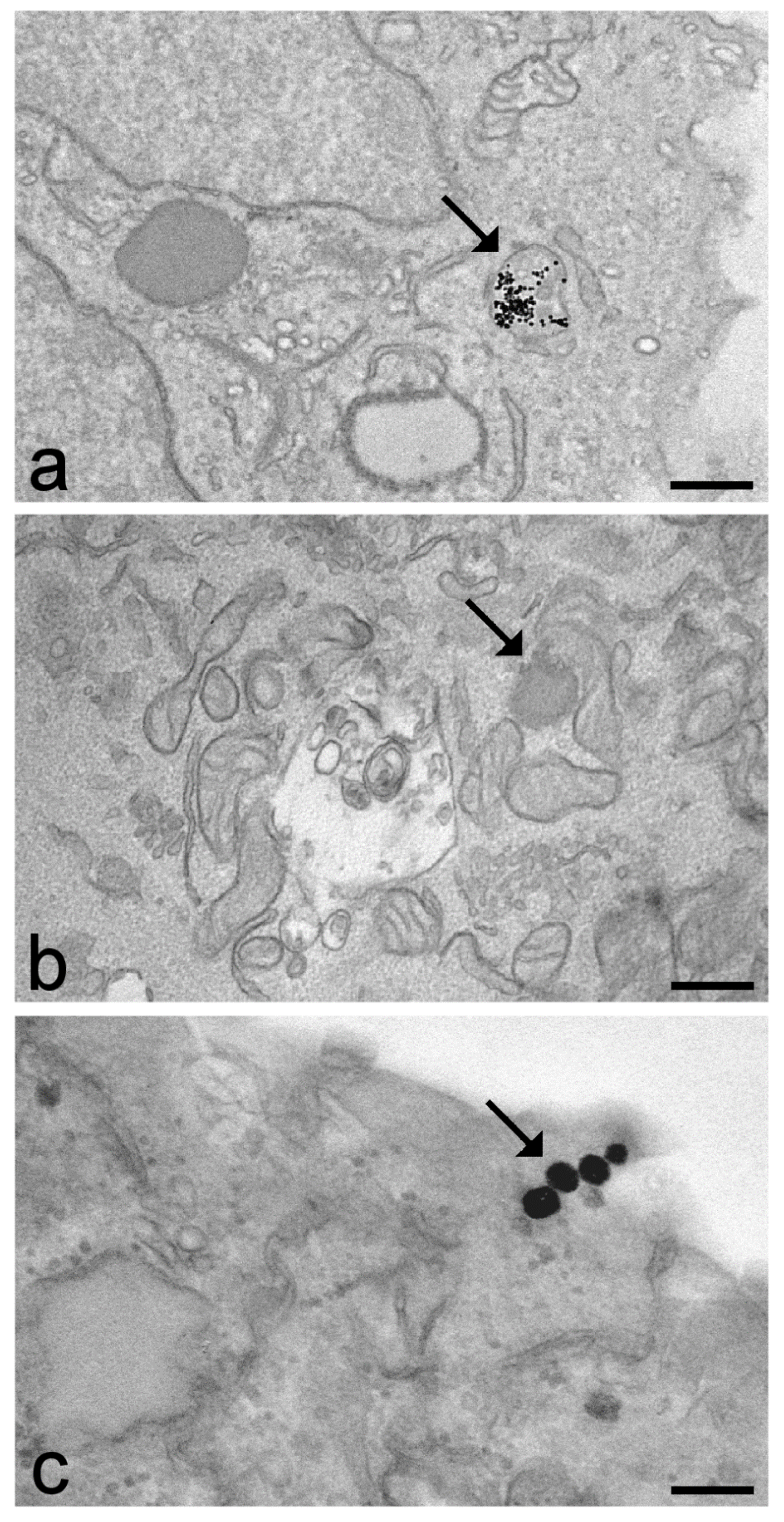
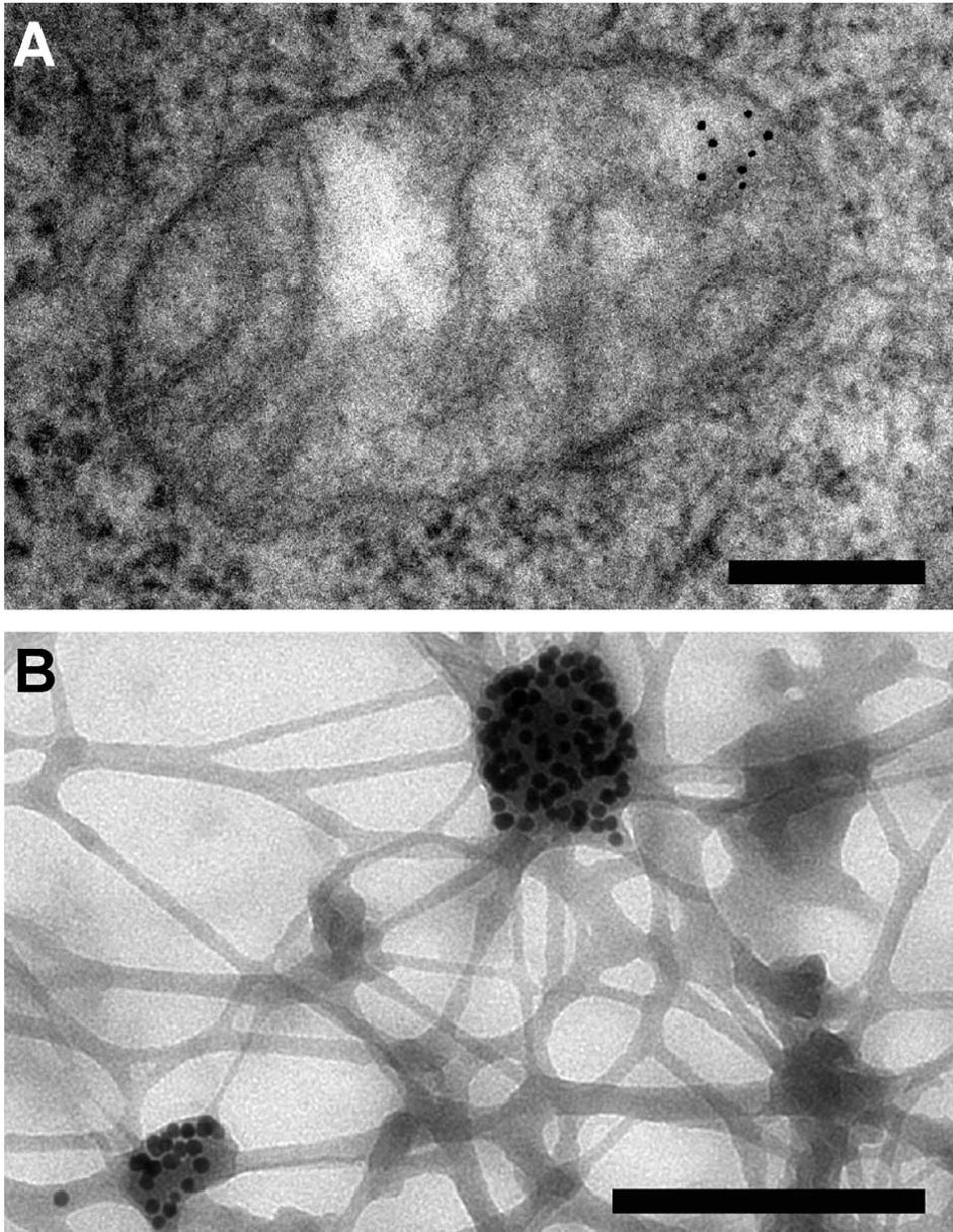
Neuron under Microscope with Labeled Diagram - AnatomyLearner Lets see the neuron histology slide labelled diagram and try to find out the below-mentioned characteristics - Presence of an identifiable cell body (soma) that locates in the brains grey matter (according to the slide image). The cell body possesses spherical, euchromatic, and large eccentric nuclei containing a prominent nucleolus. Transmission electron micrograph (TEM) identifying immunogold labeled ... (B) Immunogold labeling of ESR1 identified the protein localization at the plasma membrane, the cytosol, and the nucleus. (C) Illustrates the location of Cav-1 close to or at the plasma membrane. Chapter 14 & 15 Flashcards Flashcards | Quizlet B-cells may be stimulated to transform into memory cells. True Viruses and self-proteins are examples of proteins produced inside of the cell. True Foreign antigens presented on class I MHC molecules... Stimulate cell destruction by activated T-cells The sequence for the processing of proteins originating outside of the cell is... Transmission Electron Microscope (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The final image in a TEM is known as transmission electron micrograph. The salts of some heavy metals, e.g., lead; osmium, tungsten and uranium are often used for staining. These heavy metal stains are used to increase the contrast between ultra structures and the background. The metals can be fixed on to the specimen and is referred to as ...
Fluorescence microscope - Wikipedia Fluorescence micrograph gallery A z-projection of an osteosarcoma cell, stained with phalloidin to visualise actin filaments. The image was taken on a confocal microscope, and the subsequent deconvolution was done using an experimentally derived point spread function.
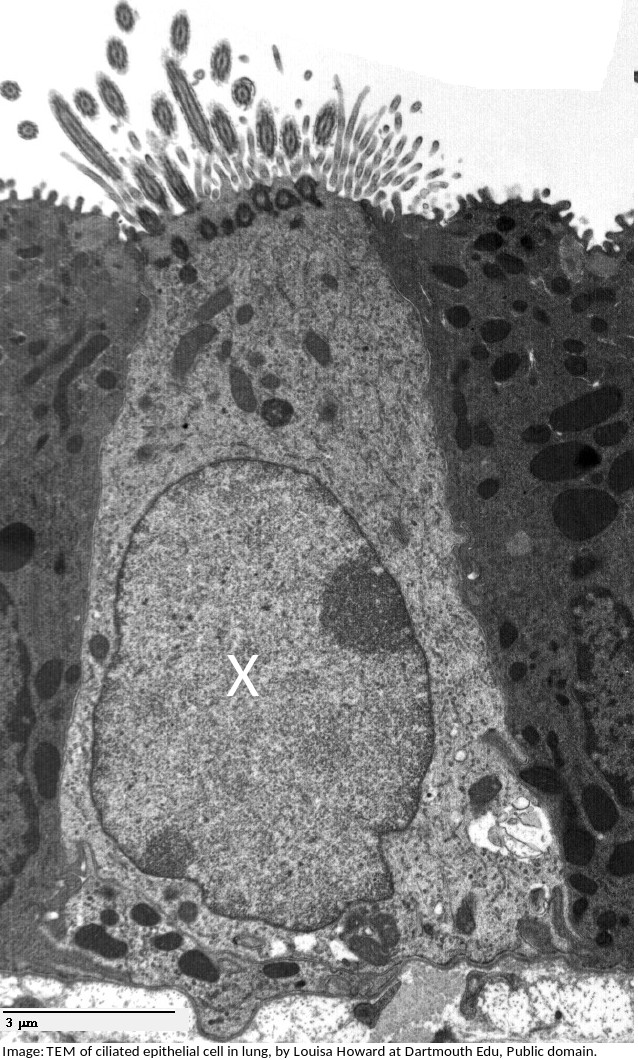
Solved Label the transmission electron micrograph of the - Chegg Question: Label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus. Nuclear envelope Nucleolus Nucleus Heterochromatin Reset Zoom This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (24 ratings)
Label This Transmission Electron Micrograph : The Corresponds To The ... Label the transmission electron micrograph of the. Transmission electron microscopy (tem) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. Interpretation of electron micrographs to identify organelles and deduce the functions of specialized cells. No microtubule labeling is evident.
Glossary - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI Bookshelf micrograph. Photograph of an image seen through a microscope. May be either a light micrograph or an electron micrograph depending on the type of microscope employed. microinjection. Injection of molecules into a cell using a micropipette. micron (m or micrometer) Unit of measurement often applied to cells and organelles.
Label This Transmission Electron Micrograph - Kaiden Brown Label This Transmission Electron Micrograph : TEM of chloroplast from Coleus blumei - Stock Image - B110 - Kaiden Brown To leave a comment, click the button below to sign in with Google. Sign in with Google Join Our Newsletter
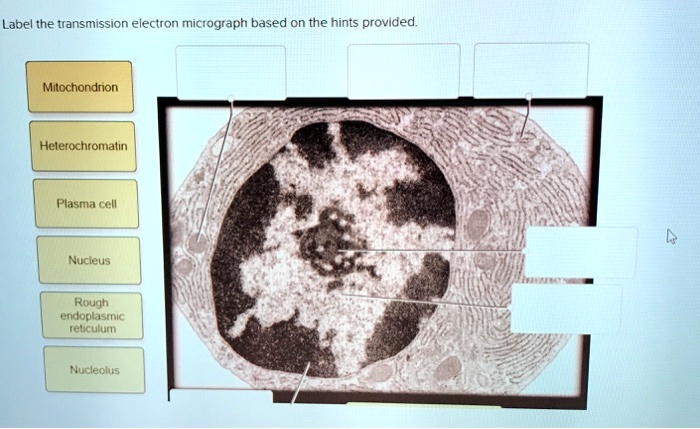
Solved Label the transmission electron micrograph of the - Chegg Transcribed image text: Label the transmission electron micrograph of the cell. 0 Nucleus rences Mitochondrion Heterochromatin Peroxisome Vesicle ULAR bumit Click and drag each label into the correct category to indicate whether it pertains to the cytoplasm or the plasma membrane.
Labeling the Cell Flashcards | Quizlet Label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus. membrane bound organelles golgi apparatus, mitochondrion, lysosome, peroxisome, rough endoplasmic reticulum nonmembrane bound organelles ribosomes, centrosome, proteasomes cytoskeleton includes microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules Identify the highlighted structures
Mesenchymal stem cell - Wikipedia Mesenchymal stem cells are characterized morphologically by a small cell body with a few cell processes that are long and thin. The cell body contains a large, round nucleus with a prominent nucleolus, which is surrounded by finely dispersed chromatin particles, giving the nucleus a clear appearance.
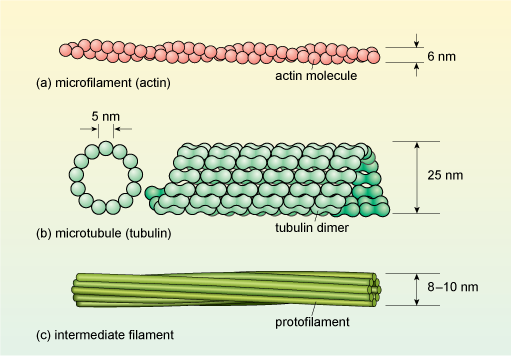
#6 Summary of Cell structure | Biology Notes for A level - Blogger Using the formula A= I/M, the actual size of an object (A) or its magnification (M) can be found if its observed (image) size (I) is measured and A or M, as appropriate, is known. All cells are surrounded by a partially permeable cell surface membrane that controls exchange between the cell and its environment.
The Transmission Electron Microscope | CCBER - UC Santa Barbara What is a Transmission Electron Microscope? Transmission electron microscopes (TEM) are microscopes that use a particle beam of electrons to visualize specimens and generate a highly-magnified image. TEMs can magnify objects up to 2 million times. In order to get a better idea of just how small that is, think of how small a cell is.
Rotavirus - Wikipedia Electron micrograph of a rotavirus infected enterocyte (top) compared to an uninfected cell (bottom). The bar = approx. 500 nm Rotaviruses replicate mainly in the gut , [74] and infect enterocytes of the villi of the small intestine , leading to structural and functional changes of the epithelium . [75]
Electron Microscopic Structure of a Typical Bacterial Cell Under electron microscope the nucleoid appears to be fibrillar and composed of a double or single stranded DNA. It has approximately 5 x l0 6 base pairs and a molecular weight of about 3 x l0 9 . The DNA molecule is approximately 1000 µm long, usually forming ring like structure or sometimes remains diffused throughout the cytoplasm of the cell.
Peripheral Nervous System | histology - University of Michigan Also, note the nucleus and cytoplasmic organelles of the Schwann cell. Remember that the myelin is part of the Schwann cell, not of the axon. 55 Peripheral nerve - Unmyelinated Nerve Fibers - Cross Section View Virtual EM Slide Unmyelinated Nerve Fibers (cross section). The axons seen in this electron micrograph are all non-myelinated.
Electron Micrographs of Cell Organelles | Zoology - Biology Discussion The Electron Micrograph of Nucleus: This is an electron micrograph of nucleus. (Fig. 17 & 18): (1) Nucleus was discovered by Brown (1831). (2) It is a characteristic entity of almost all eukaryotic cells except mammalian RBCs. (3) The nucleus is generally one but may also be two, four or many.



















Post a Comment for "41 label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus"